Architecture
What follows is a summary of the architecture and the components that are involved in running a Cartesi Compute Application, meaning some dApp that makes use of our SDK. It is convenient to start with the description of the typical ingredients involved in a decentralized application. Namely, the blockchain node and the client software.
As with any decentralized application, users are expected to have access to a blockchain node. This could be a local Ethereum node (like geth, parity or a remote one such as Infura. On the blockchain, the application logic is written in a set of dApp Smart Contracts. Moreover, the off-chain logic is executed on the Client Software, either through the internet browser (using web3) or by installing a native client. These are the typical ingredients of a decentralized application.
For an application that uses the Cartesi Compute SDK, one also needs the Cartesi Compute Infrastructure, which is composed of an on-chain and an off-chain component, as described below.
Cartesi Compute on-chain
The on-chain component of Cartesi Compute is a set of smart contracts developed by Cartesi. For convenience, the dApp developer interacts with a single one of these contracts, named "CartesiCompute". The API to interact with the Cartesi Compute smart contract is described here.
Cartesi Compute off-chain
The off-chain component of Cartesi Compute is called the Cartesi Compute Node, which plays a very similar role to the blockchain node. More precisely, in the same way that a blockchain node allows clients to interact with the first layer, a Cartesi Compute Node allows clients to interact with Cartesi.
It is expected that all validator parties (claimer and challengers) have a Cartesi Compute Node working on their behalves. In Section Topologies, we discuss alternatives to this setup.
These nodes will guarantee that their interests will be enforced on the blockchain by:
- automatically running computations;
- submitting results;
- verifying claims;
- challenging and punishing misbehavior.
All these tasks are performed automatically, with no intervention from the dApp users or even the dApp Client Software.
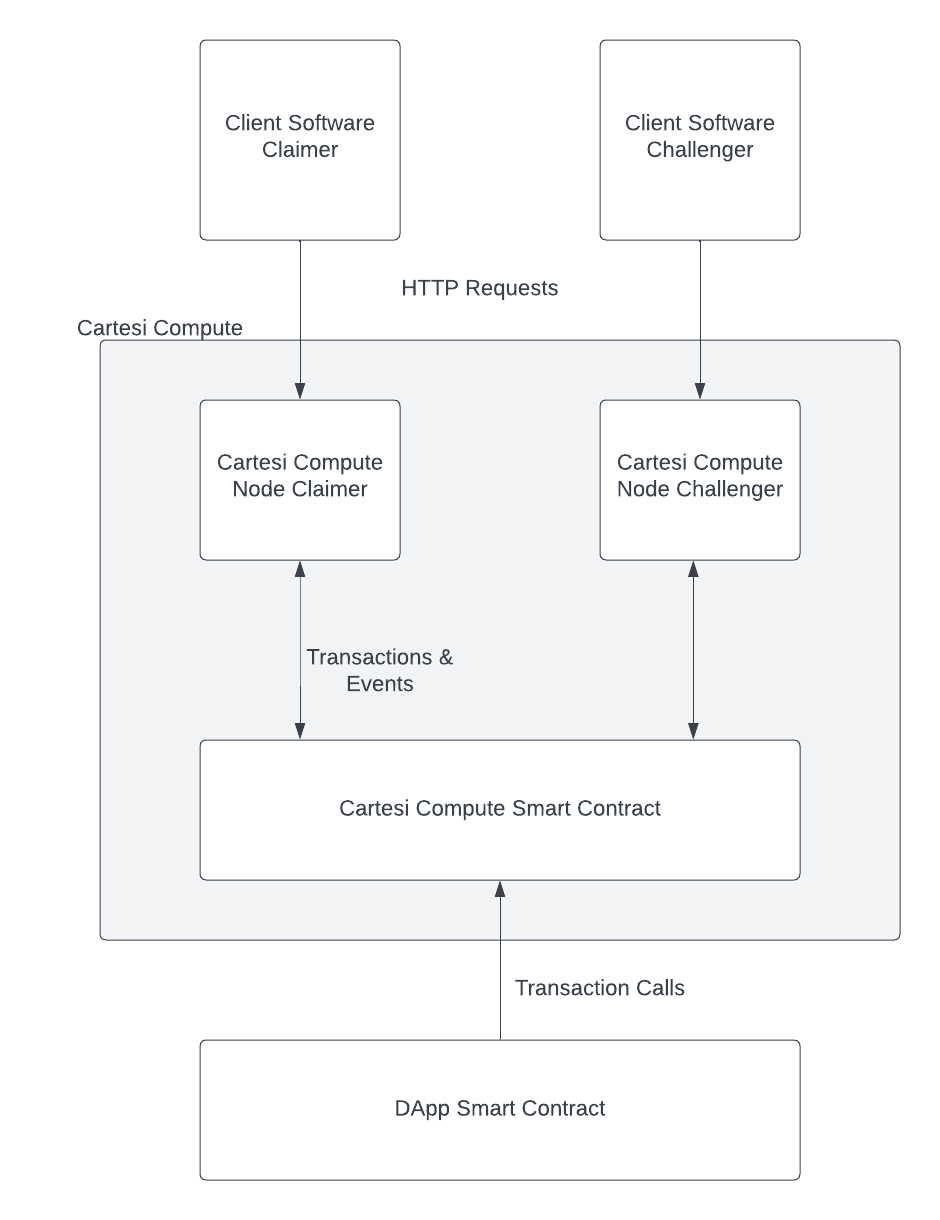
This gives a complete picture of the software components involved in running a Cartesi Compute powered dApp: The Blockchain Node, the dApp Client Software, the dApp Smart Contracts and the Cartesi Compute Node, see the above picture.