Introduction
The backend of a Cartesi dApp retrieves a new request as follows:
-
Finish — Communicates that any previous processing has been completed and that the backend is ready to handle the subsequent request. This following request is returned as the call's response and can be of the following types:
-
Advance — Provides input to be processed by the backend to advance the Cartesi Machine state. When processing an
Advancerequest, the backend can call the methods/voucher,/notice, and/report. For such requests, the input data contains the payload and metadata, such as the account address that submitted the input. -
Inspect — This function submits a query about the application's current state. When running inside a Cartesi Machine, this operation is guaranteed to leave the state unchanged since the machine is reverted to its exact previous condition after processing. For Inspect requests, the input data has only a payload.
Inspect requestsInspect requests are best suited for non-production use, such as debugging and testing. They may not function reliably in production environments, potentially leading to errors or disruptions.
-
Advance and Inspect
Here is a simple boilerplate application that handles Advance and Inspect requests:
- JavaScript
- Python
const rollup_server = process.env.ROLLUP_HTTP_SERVER_URL;
console.log("HTTP rollup_server url is " + rollup_server);
async function handle_advance(data) {
console.log("Received advance request data " + JSON.stringify(data));
return "accept";
}
async function handle_inspect(data) {
console.log("Received inspect request data " + JSON.stringify(data));
return "accept";
}
var handlers = {
advance_state: handle_advance,
inspect_state: handle_inspect,
};
var finish = { status: "accept" };
(async () => {
while (true) {
const finish_req = await fetch(rollup_server + "/finish", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({ status: "accept" }),
});
console.log("Received finish status " + finish_req.status);
if (finish_req.status == 202) {
console.log("No pending rollup request, trying again");
} else {
const rollup_req = await finish_req.json();
var handler = handlers[rollup_req["request_type"]];
finish["status"] = await handler(rollup_req["data"]);
}
}
})();
from os import environ
import logging
import requests
logging.basicConfig(level="INFO")
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
rollup_server = environ["ROLLUP_HTTP_SERVER_URL"]
logger.info(f"HTTP rollup_server url is {rollup_server}")
def handle_advance(data):
logger.info(f"Received advance request data {data}")
return "accept"
def handle_inspect(data):
logger.info(f"Received inspect request data {data}")
return "accept"
handlers = {
"advance_state": handle_advance,
"inspect_state": handle_inspect,
}
finish = {"status": "accept"}
while True:
logger.info("Sending finish")
response = requests.post(rollup_server + "/finish", json=finish)
logger.info(f"Received finish status {response.status_code}")
if response.status_code == 202:
logger.info("No pending rollup request, trying again")
else:
rollup_request = response.json()
data = rollup_request["data"]
handler = handlers[rollup_request["request_type"]]
finish["status"] = handler(rollup_request["data"])
An Advance request involves sending input data to the base layer via JSON-RPC so they can reach the dApp backend to change the application's state.
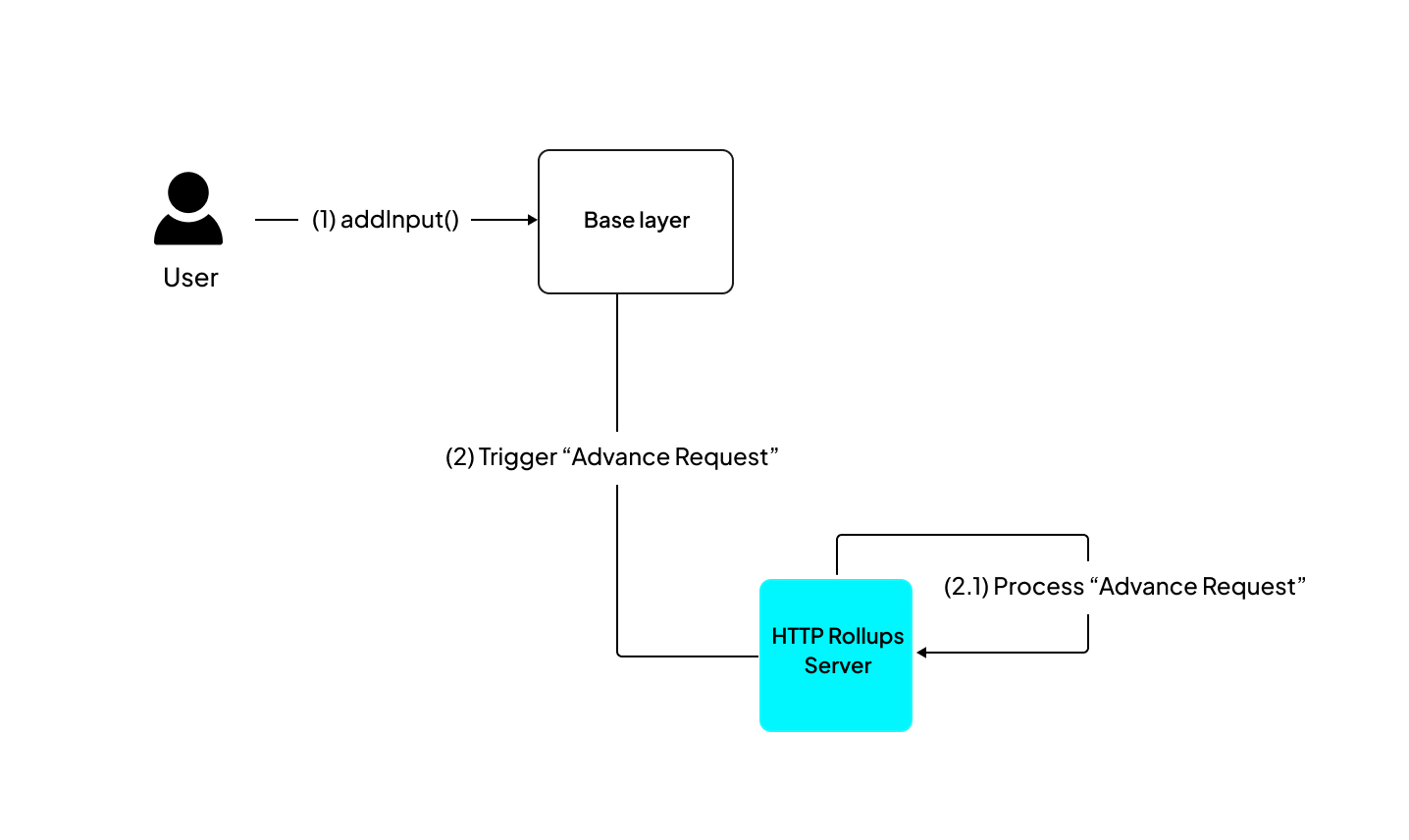
In the dApp architecture, here is how an advance request plays out.
-
Step 1: Send an input to the
addInput(address, bytes)function of the InputBox smart contract. -
Step 2: The HTTP Rollups Server reads the data and gives it to the Cartesi machine for processing.
-
Step 3: After the computation, the machine state is updated, and the results are returned to the rollup server.
An Inspect request involves making an external HTTP API call to the rollups server to read the dApp state without changing it.
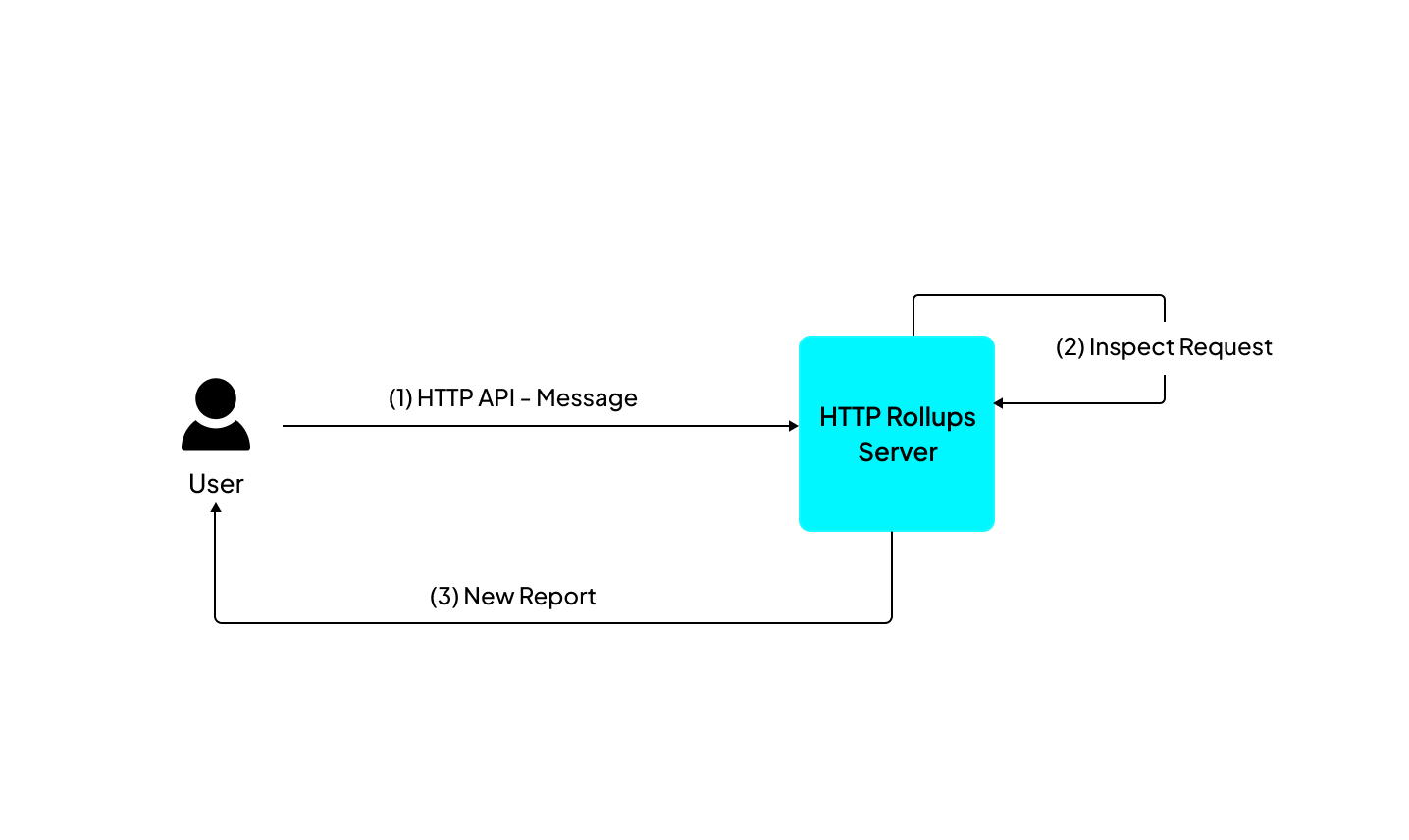
You can make a simple inspect call from your frontend client to retrieve reports.
To perform an Inspect call, use an HTTP GET request to <address of the node>/inspect/<request path>. For example:
curl http://localhost:8080/inspect/mypath
Once the call's response is received, the payload is extracted from the response data, allowing the backend code to examine it and produce outputs as reports.
The direct output types for Advance requests are vouchers, notices, and reports, while Inspect requests generate only reports.